
Dr. Marco V. Benavides Sánchez.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, the importance of effective education for medical and surgical professionals cannot be overstated. As the complexity of medical knowledge and procedures increases, traditional teaching methods often fall short in preparing healthcare practitioners for the challenges they face in real-world scenarios.
This is where active learning models come into play, providing innovative strategies that enhance training, competence, and ultimately, patient care. This article delves into the various dimensions of active learning in medical and surgical education, examining techniques, frameworks, evaluation methods, and emerging technologies that are reshaping the educational experience.
1. Active Learning Techniques in Medical Education
1.1 Multimodal Learning
One of the hallmark features of active learning is its multimodal approach, which combines various teaching methods to create a rich learning environment. Traditional lecture-based formats are being supplemented or replaced by techniques such as flipped classrooms, simulations, and hands-on practice.
Flipped Classrooms: This pedagogical model flips the traditional learning structure by allowing students to engage with lecture materials at home (often via video lectures) and reserving classroom time for interactive activities such as discussions and problem-solving exercises. Research has demonstrated that this method enhances understanding and retention of knowledge, as students arrive at class prepared to engage with the material actively.
Simulation-Based Training: High-fidelity simulations are particularly effective in teaching complex procedures. These simulations provide a controlled, risk-free environment where learners can practice and refine their skills without compromising patient safety. For instance, a study on the training of residents in central venous catheter insertion found that both multimodal active learning and traditional single-modality simulations significantly improved skills and knowledge retention. Such training methods are essential for developing not only technical skills but also decision-making and crisis management abilities.
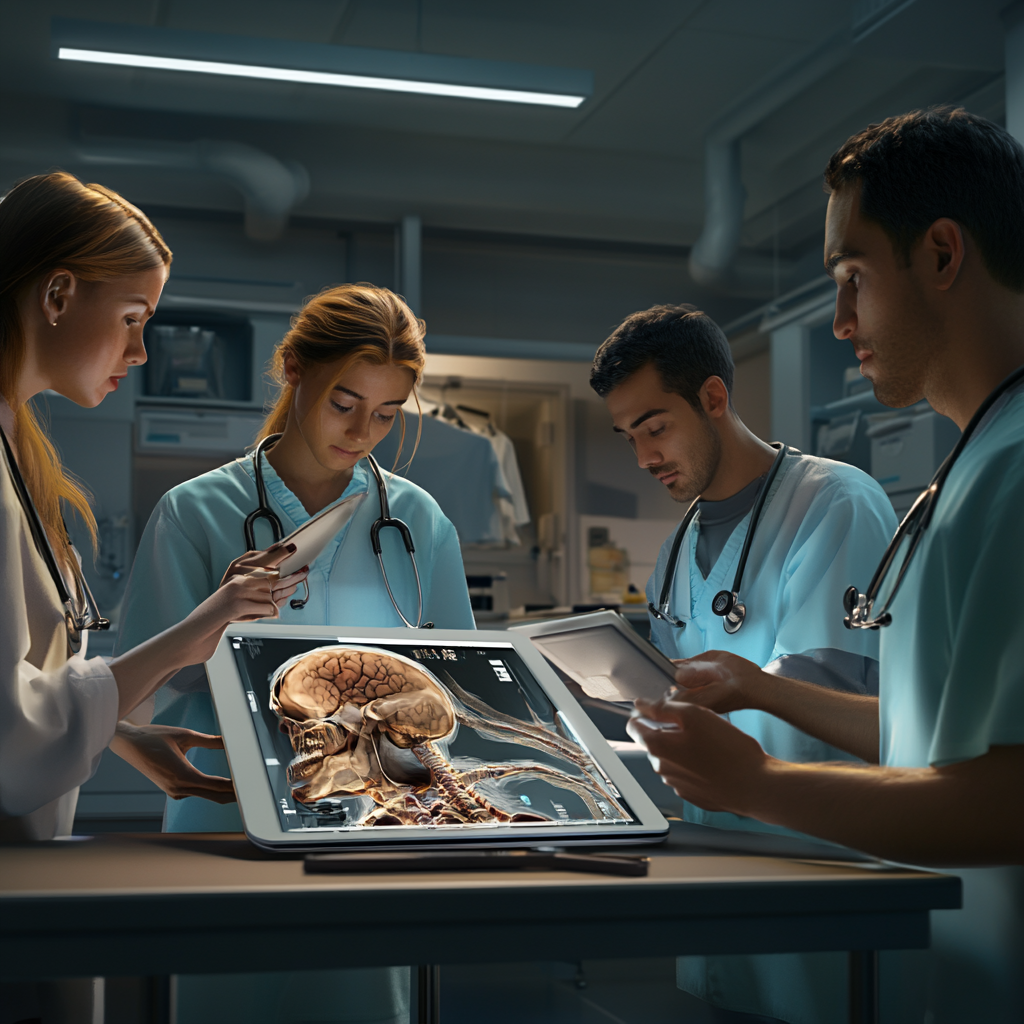

1.2 Case-Based Learning
Case-based learning is another effective technique that involves presenting learners with real-life scenarios to analyze and solve. This method encourages critical thinking and application of theoretical knowledge in practical situations. By engaging with actual case studies, learners develop a deeper understanding of patient care dynamics, medical ethics, and interprofessional collaboration.
1.3 Peer Learning and Teaching
Peer teaching, where learners educate one another, fosters collaboration and reinforces knowledge retention. Studies indicate that students who engage in peer teaching often report increased confidence and mastery of the subject matter. This approach not only benefits the “teachers” but also enhances the learning experience of their peers, creating a collaborative learning environment.
2. Surgical Training and Competence Framework
2.1 Competency-Based Training
Modern surgical education has shifted towards a competency-based training framework, which emphasizes the acquisition of both technical and non-technical skills. This approach ensures that surgeons are not only proficient in performing surgical procedures but also capable of making informed decisions in diverse clinical situations. Competency-based education focuses on measurable outcomes, allowing educators to assess learners’ readiness for independent practice.
2.2 Effective Instructional Methods
A variety of instructional methods are employed in surgical training, including:
– Learning by Doing: Engaging in hands-on practice under supervision is crucial for skill acquisition. This experiential learning process allows trainees to gain confidence and competence.
– Reflection: Incorporating reflective practices into training encourages learners to evaluate their experiences critically, fostering a deeper understanding of their strengths and areas for improvement.
– Mentoring: Experienced surgeons serve as mentors, providing guidance and feedback to trainees. This one-on-one support can significantly enhance the learning process, as mentees benefit from the mentors’ expertise and insights.
– Gaming: Simulation games and virtual scenarios can create engaging learning experiences, encouraging competition and teamwork among participants while reinforcing skills and knowledge.
3. Evaluation and Outcomes
3.1 Performance Metrics
Evaluating the effectiveness of active learning models is essential for continuous improvement in educational practices. Common performance metrics include:
– Knowledge Retention: Assessing how well learners retain information over time provides insight into the efficacy of teaching methods.
– Skill Acquisition: Objective assessments of technical skills—such as through direct observation or practical exams—can determine the impact of training on learners’ abilities.
– Learner Satisfaction: Surveys and feedback tools can gauge learner satisfaction, providing valuable insights into their experiences and perceptions of the educational interventions.
3.2 Clinical Outcomes
While much of the research on active learning has focused on skill acquisition and knowledge retention, there is an increasing interest in understanding how these educational strategies translate into improved clinical outcomes. Studies are beginning to explore the links between active learning methodologies and patient care, aiming to establish a clear connection that underscores the importance of effective training.
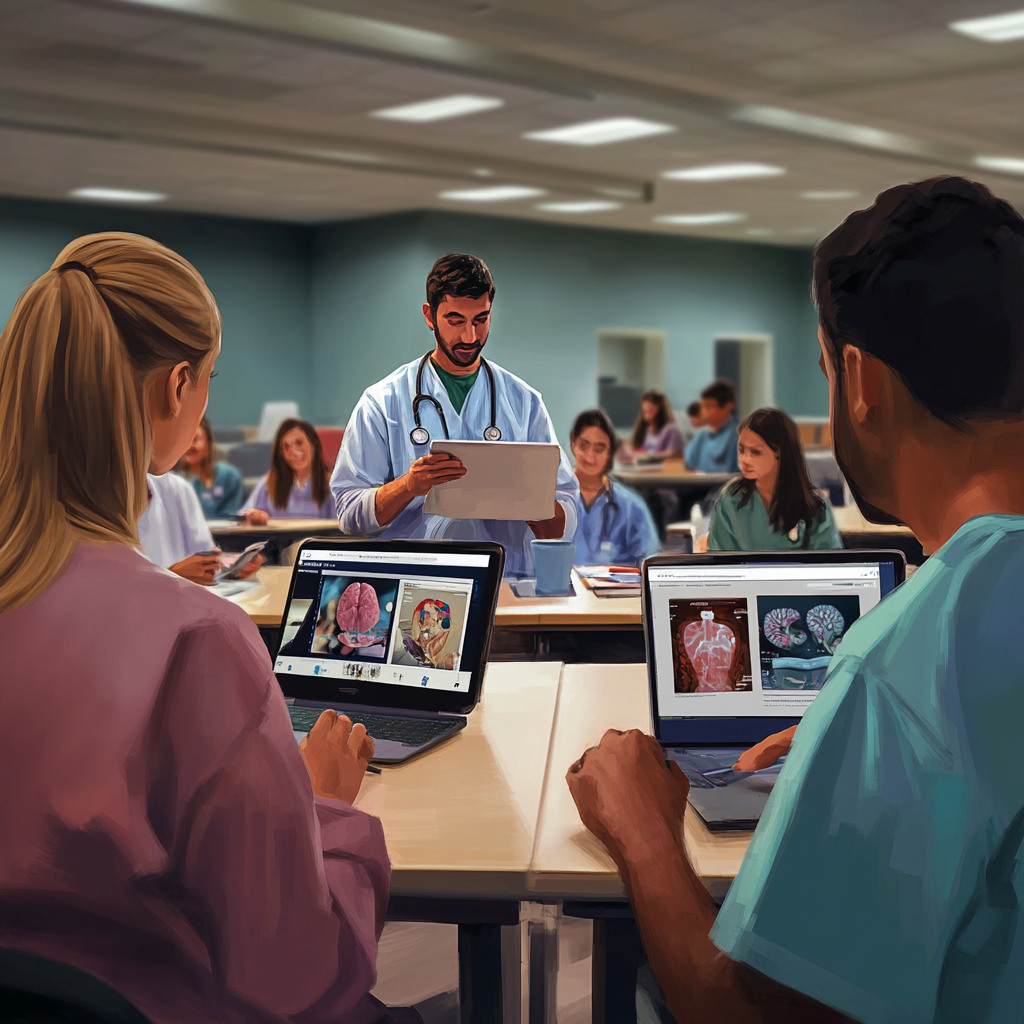

3.3 Longitudinal Studies
Conducting longitudinal studies can provide insight into the long-term impacts of active learning on clinical performance and patient care. These studies can help educators identify which teaching methods yield the best outcomes and refine training programs accordingly.
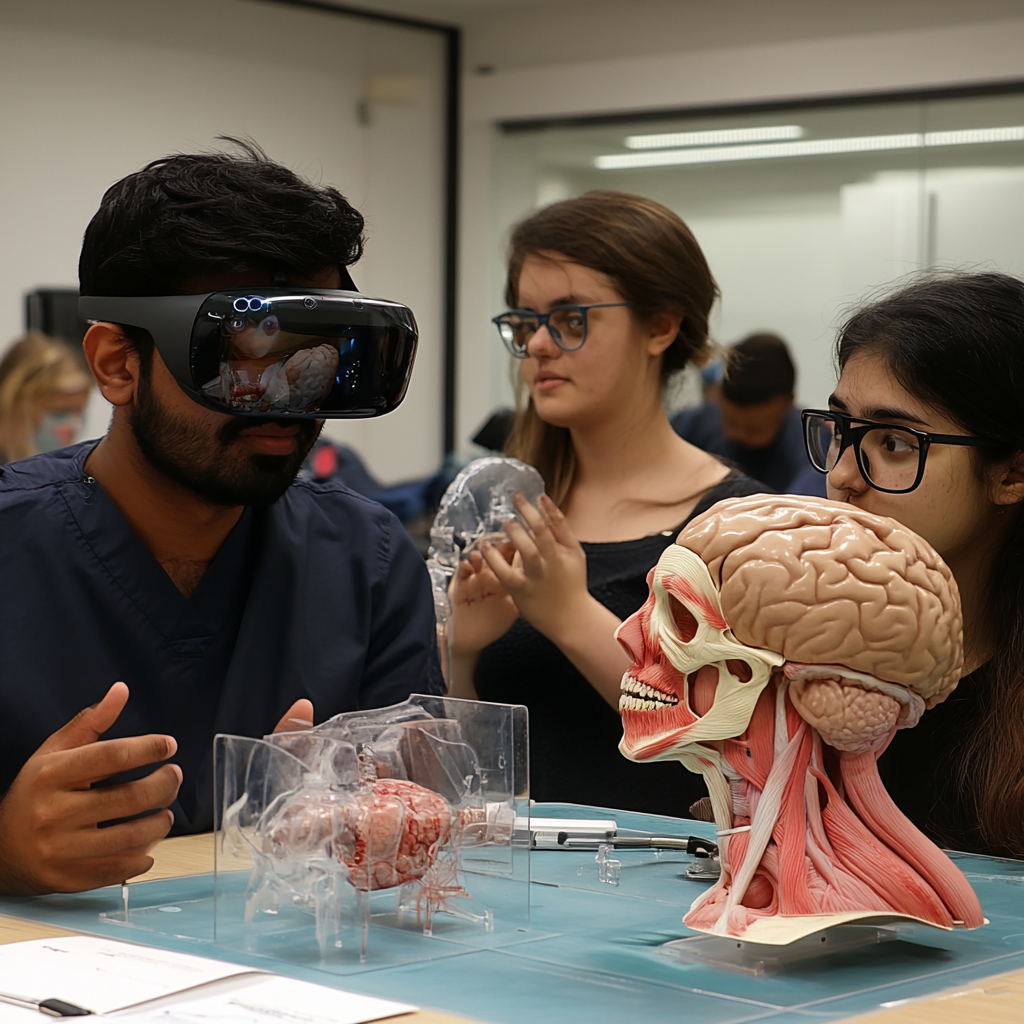
4. Extended Reality (XR) in Medical Education
4.1 Virtual and Augmented Reality
The integration of Extended Reality (XR) technologies—encompassing both virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)—is revolutionizing medical education. XR technologies offer immersive learning experiences that simulate real-life scenarios, allowing learners to practice procedures in a controlled virtual environment.
Benefits of XR:
– Safe Learning Environment: XR provides a risk-free platform for learners to experiment and make mistakes, fostering a deeper understanding of procedures without the fear of harming patients.
– Enhanced Engagement: The immersive nature of XR captures learners’ attention and encourages active participation, leading to improved retention and understanding.
– Accessibility: XR can make advanced training accessible to a broader audience, enabling more learners to gain exposure to complex procedures without the constraints of physical resources.
4.2 Real-Time Feedback
Some XR platforms are equipped with real-time performance analytics, allowing learners to receive immediate feedback on their actions. This instant feedback loop can significantly enhance the learning experience, helping learners recognize their mistakes and correct them on the spot.
Future Directions
To fully realize the potential of active learning in medical education, several future directions warrant attention:
– Integrating Artificial Intelligence: AI technologies can play a crucial role in evaluating learner performance and providing personalized feedback, further enhancing the learning experience.
– Expanding Research: Continued research into the long-term effects of active learning on clinical outcomes will be vital for validating these educational methods and ensuring they meet the needs of modern healthcare.
– Promoting Interprofessional Learning: Encouraging collaboration among different healthcare disciplines can enhance team-based care training, preparing learners for the collaborative nature of modern medical practice.
Conclusion
Active learning models are significantly transforming medical and surgical education, providing more interactive, engaging, and effective training methods. By emphasizing multimodal learning, competency-based training, and the integration of emerging technologies such as XR, these approaches aim not only to enhance the learning experience but also to improve clinical competence and patient outcomes.
The shift towards active learning is a response to the complex demands of modern healthcare, ensuring that medical professionals are well-equipped to navigate the intricacies of patient care. As educational methodologies continue to evolve, ongoing research and adaptation will be essential to maximize the benefits of active learning in training the next generation of healthcare professionals.
For further reading:
(1) Comparison of multimodal active learning and single-modality procedural ….
(2) What are the learning objectives in surgical training – a systematic ….
(3) Use of Extended Reality in Medical Education: An Integrative Review.
(4) Active Learning in Medical Education: Application to the Training of ….
#Tecnomednews #Emedmultilingua #Medmultilingua

Leave a Reply