By Dr. Marco V. Benavides Sánchez.
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a key tool in the transformation of modern medicine. Technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and large language models (LLMs) have enabled significant advancements in clinical diagnosis, drug discovery, and patient care. This article explores the foundations of AI and its current application in optimizing medical and surgical processes.
What is Artificial Intelligence and How Does It Work?
Artificial intelligence refers to the ability of machines to simulate human cognitive processes such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. Its application in medicine is based on three fundamental pillars:
1. Machine Learning: It uses algorithms to analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions. For example, it can analyze clinical histories to predict disease risks.
2. Deep Learning: An advanced branch of machine learning that employs neural networks to process large volumes of data, such as medical and genomic images, with high precision.
3. Large Language Models: Recently developed systems that process and generate text with a level of understanding and fluency similar to humans. In medicine, they can analyze electronic health records (EHRs) or assist in patient education.

Applications of AI in Modern Medicine
The incorporation of AI in the medical field has led to advances that optimize patient care and improve clinical outcomes. These are some of its most notable applications:
1. Disease Diagnosis
AI has become an indispensable tool for the early and accurate diagnosis of diseases. For example:
– Medical Imaging: Deep learning algorithms can analyze X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to detect lesions or tumors with sensitivity and specificity surpassing human doctors.
– Genomics: AI analyzes genetic data to identify mutations associated with hereditary diseases or predict responses to pharmacological treatments.

2. Treatment Optimization
AI is also used to design personalized treatment plans. With the help of massive data, AI systems can:
– Identify effective therapies for specific diseases.
– Adjust drug dosages based on patient characteristics.
– Predict complications and potential outcomes.
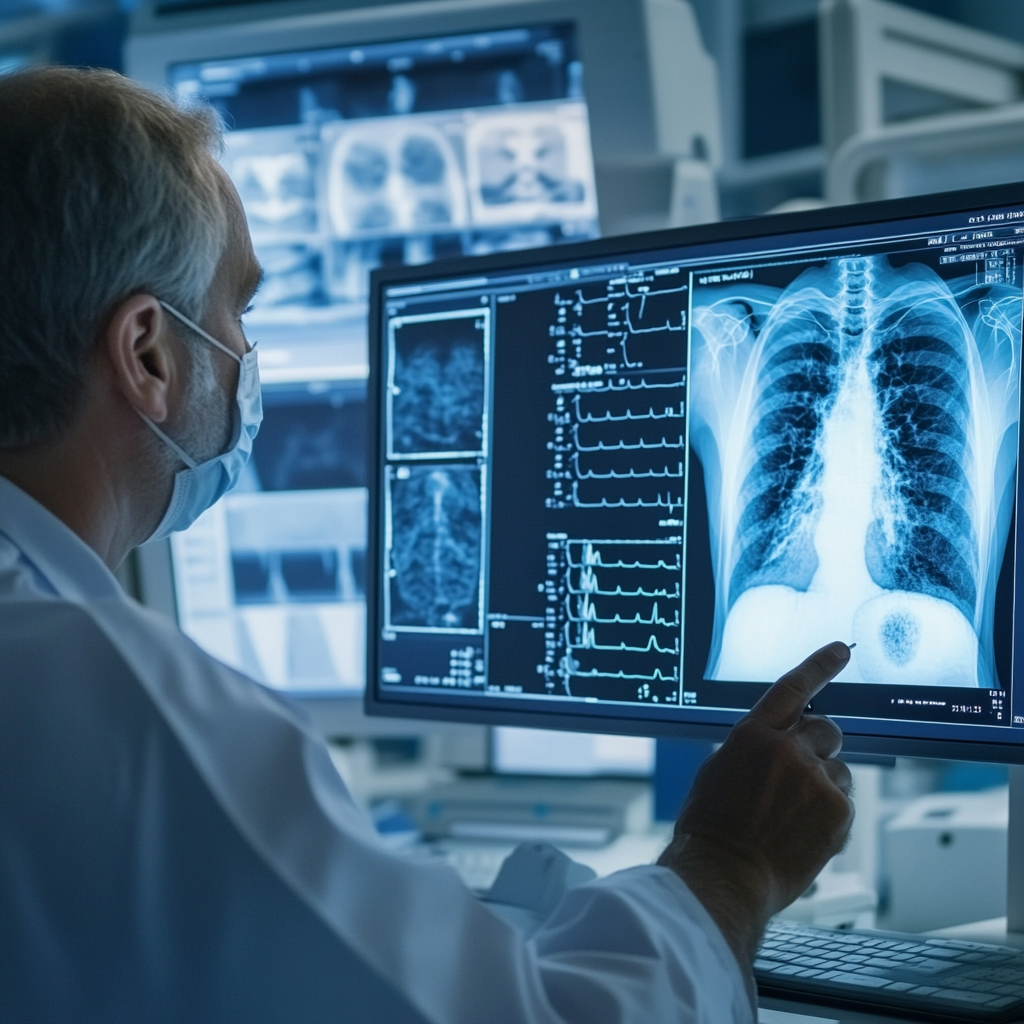
3. Surgical Support
AI is redefining surgery with tools such as:
– Robotic Surgery: Systems like the da Vinci, assisted by AI, improve precision and reduce the risk of errors during complex procedures.
– Surgical Planning: Algorithms analyze preoperative images to identify the best surgical strategy.

4. Workflow Management
In healthcare systems, AI helps manage resources and optimize processes, such as:
– Prioritizing patients in emergency rooms.
– Predicting demand for hospital beds and resources.
– Identifying gaps in care to improve efficiency.

Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Although the applications of AI are promising, they also present important challenges:
– Data Privacy: The use of large volumes of medical data raises concerns about security and regulatory compliance.
– Transparency: AI models often operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand their decisions.
– Equity: It is crucial to ensure that AI systems do not perpetuate biases that could negatively impact certain patient groups.

The Future of AI in Medicine
As technology advances, AI is expected to play an even more central role in medicine. Promising areas include:
– Predictive Medicine: With more refined algorithms, AI will be able to predict the likelihood of developing chronic diseases with greater accuracy.
– Drug Discovery: AI accelerates the development of new drugs by identifying promising compounds and simulating clinical trials.
– Digital Health: Wearable devices connected to AI systems will be able to monitor health in real-time and alert patients about anomalies.

Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing medicine by providing tools that enhance diagnosis, personalize treatments, and optimize surgical processes. However, its full adoption requires addressing ethical challenges, ensuring equity in its application, and fostering collaboration between technology and the medical profession. Over time, AI promises not only to transform medical practice but also to significantly improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
References
1. Khera, R., Butte, A. J., Berkwits, M., Hswen, Y., Flanagin, A., Park, H., Curfman, G., & Bibbins-Domingo, K. (2023). AI in Medicine—JAMA’s Focus on Clinical Outcomes, Patient-Centered Care, Quality, and Equity. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.15481. Retrieved from JAMA Network.
2. Katwaroo, A. R., Adesh, V. S., Lowtan, A., & Umakanthan, S. (2024). Diagnostic, therapeutic, and ethical impact of artificial intelligence in modern medicine. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 100(1183), 289-296. https://doi.org/10.1093/postmj/qgad135. Retrieved from Oxford Academic.
3. Secinaro, S., Calandra, D., Secinaro, A., Muthurangu, V., & Biancone, P. (2021). The role of artificial intelligence in healthcare: A structured literature review. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 21, Article number: 125. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-021-01488-9. Retrieved from BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.
4. Xie, Y., Zhai, Y., & Lu, G. (2024). Evolution of artificial intelligence in healthcare: A 30-Year bibliometric study. Frontiers in Medicine. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2024.1505692. Retrieved from Frontiers in Medicine.


Leave a Reply